Understanding Medical Cannabis: A Guide for Healthcare Practitioners
Medical
cannabis is becoming an increasingly relevant topic in the healthcare sector,
particularly as it pertains to the treatment of chronic conditions in elderly
patients. The use of medical cannabis can offer significant benefits, including
pain relief and improved quality of life. The following describes some of what
can be learned in the program, Medical Cannabis in the Elderly presented by,
Dr. Vu Kiet Tran.
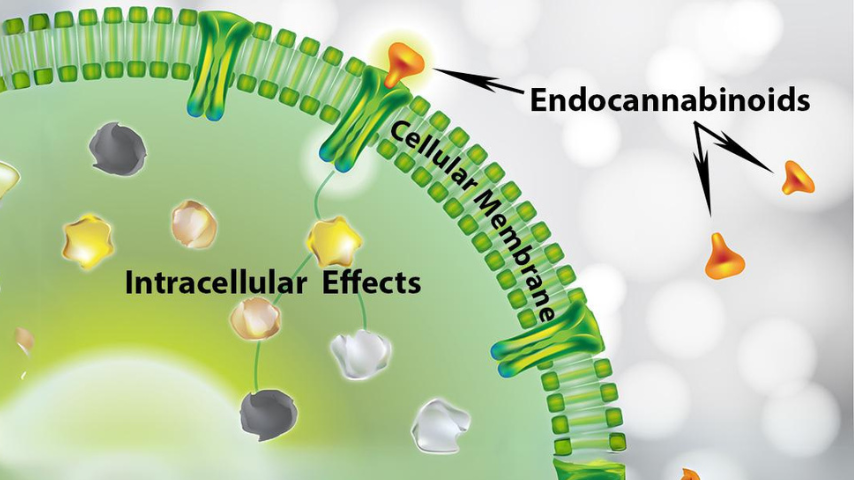
The Endocannabinoid System
The Endocannabinoid system plays a crucial role in regulating pain by modulating the transmission of pain signals in the nervous system.
When the body experiences pain, endocannabinoids are released and bind to CB1 receptors in the brain and spinal cord, which can inhibit the release of neurotransmitters and reduce the perception of pain. Additionally, CB2 receptors, primarily located in immune cells, help to manage inflammation, which is often a source of chronic pain. By balancing these processes, the ECS can naturally reduce pain sensations and inflammation, making it a key target for medical cannabis in pain management.
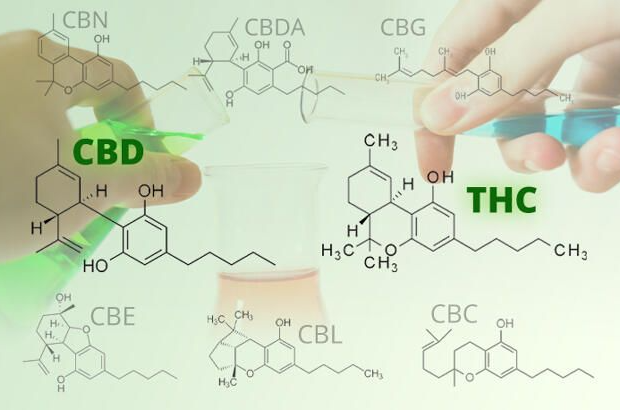
Active Compounds in Cannabis and Their Uses
Cannabis
contains over 100 different cannabinoids, with THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and
CBD (cannabidiol) being the most studied and utilized. Each cannabinoid has
unique properties that make it suitable for different medical applications:
THC
Known for its psychoactive
effects, THC can relieve pain, reduce nausea and vomiting, stimulate appetite,
and improve sleep. It is particularly effective in treating chronic pain,
multiple sclerosis, and cancer-related symptoms.
CBD
Non-psychoactive, CBD is
renowned for its anti-inflammatory, anti-anxiety, and seizure-reducing
properties. It is often used in combination with THC to mitigate the
psychoactive effects while enhancing therapeutic benefits.
Combining THC and CBD can have synergistic effects, enhancing the therapeutic potential while minimizing adverse effects. For elderly patients, formulations with a higher ratio of CBD to THC (e.g., 25:1 or 5:1) are often recommended to avoid psychoactive effects while providing symptom relief.
Indications for Medical Cannabis
Medical cannabis is not a one-size-fits-all solution and should be prescribed based on a thorough evaluation of the patient's condition, medical history, and potential risks. Some well-supported indications for medical cannabis include:
Chronic Pain
Medical cannabis can be an
effective monotherapy or adjunct therapy for chronic pain management,
particularly for neuropathic and musculoskeletal pain.
Multiple Sclerosis
It can help manage chronic pain and spasticity associated with multiple sclerosis.
Sleep Disorders
THC can improve sleep
quality, which is particularly beneficial for patients suffering from chronic
pain or other conditions that disrupt sleep.
Anorexia and Cachexia
Medical cannabis can stimulate appetite and promote weight gain.
Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea & Vomiting
THC is effective in
reducing nausea and vomiting in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy.
Contraindications to consider:
-
Patients Under 25: Due to the potential impact on brain development.
-
Cardiopulmonary Conditions: Such as severe heart disease or respiratory disorders, especially if the patient smokes or vapes cannabis.
-
History of Psychiatric Disorders: Including schizophrenia or severe anxiety, which could be exacerbated by THC.
-
Concurrent Use of Anticoagulants: Medical cannabis can interact with blood thinners, increasing the risk of bleeding.
-
Severe Liver or Kidney Disease: Impaired liver or kidney function can alter cannabinoid metabolism and excretion, leading to increased risk of side effects or toxicity.
Stay Ahead with the Latest in Medical Education

Copyright ICI Engage© 2023-2025
Site
Write your awesome label here.
Empty space, drag to resize
Anaphylaxis Outpatient Management
Learning Objectives
-
Discuss with patients the priority role of epinephrine in the treatment of anaphylaxis
-
Describe the various epinephrine auto-injectors on the Canadian market
-
Understand how shared decision making can contribute to better preparedness for the management of anaphylaxis
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
Advanced Management of Allergic Rhinitis
Learning Objectives
-
Optimize the management of allergic rhinitis (AR) in preventing and controlling symptoms
-
Confidently identify patients who are candidates for allergen specific immunotherapy
-
Conduct a shared decision making discussion with patients about the various treatment options for management of AR
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
Anaphylaxis Myths and Realities
Learning Objectives
-
Recognize what does and does not constitute an anaphylactic reaction
-
Address several common myths about anaphylaxis
-
Confidently manage your patients living with a risk of anaphylaxis
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
Antihistamine Updosing
Learning Objectives
-
Discuss with patients the priority role of epinephrine in the treatment of anaphylaxis
-
Describe the various epinephrine auto-injectors on the Canadian market
-
Understand how shared decision making can contribute to better preparedness for the management of anaphylaxis
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
Let's Talk Canadian Guidelines Conference
Learning Objectives
-
To discuss the immunization guidelines and recommendations in Canada
-
To explore the migraine preventive strategies and discuss the latest migraine preventive recommendations in Canada.
-
To recognize the importance of an integrated and harmonized people-centered approach for cardiovascular-metabolickidney syndrome in people living with and without diabetes.
-
To explain the evolving nomenclature for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and describe current best practices for diagnosing and managing this condition.
-
To evaluate the risks and harms from alcohol consumption and summarize the recommendations to reduce alcohol related risks.
-
To compare the asthma and COPD guidelines and distinguish between the available treatment options.
-
To deliberate on the potential benefits and risks of introducing AI into medicine.
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
Dementia: Assessment of Cognition and Diagnosis
Learning Objectives
-
Review the risk factors and possible presentations of dementia in older adults
-
Understand the recommended processes for family physicians to follow in the evaluation of individuals with suspected dementia
-
Distinguish between dementia and other conditions which may present with cognitive changes in older adults
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
Initial Management of Dementia
Learning Objectives
-
Develop and approach to the disclosure of a diagnosis of dementia
-
Understand the nonpharmacological management of early dementia including care partner supports
-
Review the indications and potential side-effects of medications approved for dementia (cholinesterase inhibitors, memantine)
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
Financial Literacy and Burnout in Physicians
Learning Objectives
-
Describe which financial stresses most commonly affect physicians
-
Describe how the financial stress is linked to burnout
-
Devise a plan to financial healing
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
Highlighting Obesity Week & Effective Management Strategies for Primary Care
Learning Objectives
-
Discuss the impact of obesity today, emerging perspectives and management strategies
-
Simplify new clinical data into effective conversations for primary care
-
Review highlights from Obesity Week 2023
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
Improving Allergy Management: Putting Benadryl to Bed
Learning Objectives
-
Describe the risks of 1st generation antihistamines
-
Counsel patients about the importance of avoiding 1st generation agents.
-
Confidently select an appropriate 2nd generation antihistamine alternative for your patients
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
Semaglutide, Cardiovascular Disease and Obesity: Key Insights from the SELECT Trial
Learning Objectives
-
Review the pathophysiology of Obesity and CV disease
-
Discuss current and future CVOTs in Obesity
-
Review highlights of the SELECT Trial
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
Three "Must Do" Behaviour Treatment Principles to Pair with Anti-Obesity Medications
Learning Objectives
Discuss the "Must Do" behavior treatment principles to pair with anti-obesity medications, specifically:
-
Internalized Weight bias (IWB)
-
Weight Expectations
-
Appetite/Wanting
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
Point of Care: Ambulatory Glucose Monitoring
Learning Objectives
-
Understand why ambulatory glucose monitoring (AGM) an important consideration for patients is living with Diabetes
-
Describe which patients will benefit the most from ambulatory glucose monitoring systems
-
Explain how technology empowers patients to make informed choices about their health
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
Point of Care: Ambulatory Glucose Monitoring - It's All About the AGP
Learning Objectives
-
Assess how easy Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) technology is to implement into patient care
-
Recognize how CGM empowers patients to make better choices and enables positive change
-
Appreciate how easy the ambulatory glucose profile is to interpret and how that informs care decisions
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
Point of Care: surveillance continue du glucose
Thème
-
Quels sont les patients qui pourraient bénéficier de systèmes de surveillance du glucose en continu ?
-
Comment ces technologies peuvent-elles responsabiliser les patients?
-
La différence entre le glucose interstitiel et le glucose capillaire et la valeur que ces dispositifs apportent aux patients et aux prestataires de soins.
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
Point of Care: Anaphylaxis
Learning Objectives
-
Review the priority role of epinephrine
-
Discuss shared decision making
-
Selecting the appropriate EAI
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
Medical Cannabis in the Elderly
Learning Objectives
-
The Endocannabinoid System 101
-
What is medical cannabis: components, formulations
-
Indications for use in the elderly/long term care population
-
Challenges in prescribing in Long Term Care
Empty space, drag to resize
About 15 Minute Fridays
15 Minute Fridays is a video series that provides quick, impactful learning in the same length of time as your coffee break.
Designed for healthcare professionals, 15MF episodes will give you practical insights for your everyday practice.
New episodes released every Friday.
Designed for healthcare professionals, 15MF episodes will give you practical insights for your everyday practice.
New episodes released every Friday.

Subscribe to be notified about new episodes!
À propos des Vendredis Express : 15 min top chrono!
Vendredis Express : 15 min top chrono est une série de vidéos qui permet un apprentissage rapide et efficace en l'espace d'une pause-café.
Conçus pour les professionnels de la santé, les épisodes des vendredis express vous apporteront des informations pratiques pour votre pratique quotidienne.
De nouveaux épisodes sont publiés chaque vendredi.
Conçus pour les professionnels de la santé, les épisodes des vendredis express vous apporteront des informations pratiques pour votre pratique quotidienne.
De nouveaux épisodes sont publiés chaque vendredi.

Abonnez-vous pour être informé des nouveaux épisodes !
Thank you!
Empty space, drag to resize
An Efficient Approach to Addressing Syncope in the Office
Learning Objectives
-
Evaluate patients who present with syncope to determine cardiac or noncardiac causes.
-
Identify the risk factors for sudden cardiac death.
-
Analyze the evidence surrounding the use of ECG and CT scans in the assessment of a patient with syncope.
-
Perform a differential diagnosis to identify or rule out cardiac causes of syncope.
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
vendredi express : 15 min top chrono !
Le trouble dépressif majeur : Outils de diagnostic et de traitement
Objectifs d'apprentissage
-
Définir les outils appropriés pour diagnostiquer une dépression majeure, écarter les maladies concomitantes et mesurer la symptomatologie.
-
Appliquer des stratégies fondées sur des preuves pour choisir les antidépresseurs selon les symptômes des patients et ajuster le traitement en cas de réponse insuffisante (augmentation, changement ou ajout de traitements d’appoint).
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
15 minute fridays
Major Depressive Disorder: Tools for Diagnosis and Treatment
Learning Objectives
-
Identify appropriate tools to diagnose major depressive disorder, rule out comorbidities, and measure symptomology.
-
Apply evidence-based strategies to choose antidepressants based on patient-specific symptoms and to address poor treatment responses with augmentations, switching or adjunctive therapies.
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
15 minute fridays
Major Depressive Disorder: Functioning at Work and Beyond
Learning Objectives
-
Recognize the key steps for responding to patients requesting sick notes for time off work
-
Identify evidence-based assessments and guidelines that can be used to support patient management and care
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
vendredi express : 15 min top chrono !
Trouble dépressif majeur : optimiser le fonctionnement au travail et ailleurs
Objectifs d'apprentissage
-
Déterminer les principales étapes à suivre pour répondre aux patients qui demandent un arrêt de travail pour cause médicale
-
Cibler les évaluations et les lignes directrices fondées sur des données probantes qui peuvent être utiles dans la prise en charge et les soins des patients
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
Sign Up for our Newsletter
Empty space, drag to resize
Wake Up to Better Allergy Care: Practical Approaches for Early Control of AR
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this accredited learning program, participants will be able to:
Clinical Evaluation & Diagnosis:
-
Apply evidence-based guidelines to differentiate between seasonal and perennial allergic rhinitis.
-
Identify when to order both serum-specific IgE testing and skin prick testing to confirm allergen sensitivities.
-
Recognize the limitations of symptom history alone in diagnosing allergic rhinitis and the role of objective testing.
Optimize Treatment Strategies:
-
Differentiate between monotherapy and combination therapy options for allergic rhinitis, based on patient presentation and evidence-based recommendations.
-
Justify the use of intranasal corticosteroid (INCS) and intranasal antihistamine (INAH) combination therapy over monotherapy or second-generation oral antihistamines.
-
Evaluate the appropriate use of sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) versus pharmacologic interventions in the management of allergic rhinitis.
Enhance Patient Adherence & Counseling:
-
Effectively counsel patients on the proper technique and adherence strategies for nasal spray use.
-
Address common patient concerns and misconceptions regarding nasal spray discomfort, dependence, and efficacy.
-
Implement motivational interviewing and shared decision-making techniques to encourage adherence to optimal therapy.
Understand Interdisciplinary Collaboration & Referral Criteria:
-
Recognize when to refer patients with persistent allergic rhinitis to allergy specialists for further evaluation or immunotherapy.
-
Collaborate effectively within an interdisciplinary team to ensure optimal patient outcomes, including pharmacist-led medication adherence support.
-
Identify key barriers to effective treatment adherence and implement strategies to address them at the primary care level.
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
15 minute fridays
From Congestion to Clarity: Managing Allergic Rhinitis Effectively
Learning Objectives
-
Understand the prevalence and impact of allergic rhinitis.
-
Identify common triggers and seasonal variations in symptoms.
-
Review effective treatment options for allergic rhinitis.
-
Explore the role of immunotherapy in disease management.
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
vendredi express : 15 min top chrono !
De la congestion au soulagement : gérer la rhinite allergique efficacement
Objectifs d'apprentissage
-
Comprendre la prévalence et les conséquences de la rhinite allergique.
-
Cibler les déclencheurs courants et les variations saisonnières des symptômes.
-
Passer en revue les options de traitement efficaces pour le traitement de la rhinite allergique.
-
Examiner le rôle de l’immunologie dans la prise en charge de la maladie.
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
15 minute fridays
Abdominal POOP (Pain out of Proportion)
Learning Objectives
-
Recognizing POOP as a Red Flag
-
Major Abdominal POOP Conditions Discussed: Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) and Ischemic Bowel (Acute Mesenteric Ischemia)
-
Avoiding Diagnostic Pitfalls
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
vendredi express : 15 min top chrono !
Douleurs abdominales disproportionnées
Objectifs d'apprentissage
-
Reconnaître la douleur disproportionnée comme un signal d’alarme )
-
Discuter des principales affections qui se manifestent par des douleurs abdominales disproportionnées : Anévrisme de l’aorte abdominale (AAA) et Infarctus intestinal (ischémie mésentérique aiguë)
-
Éviter les pièges liés au diagnostic
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
Cognitive Bias in Medical Decision-Making: Enhancing Clinical Judgment in Primary Care
Learning Objectives
-
Recognize the impact of cognitive biases on clinical decision-making.
-
Identify common biases that influence diagnosis, treatment, and patient interactions.
-
Apply metacognitive strategies to mitigate bias in real-world medical scenarios.
-
Utilize evidence-based decision-making techniques to enhance diagnostic accuracy and reduce errors.
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
15 minute fridays
HPV Testing and Immunization: A Combined Approach to Patient Care
Learning Objectives
-
Recognize the importance of HPV prevention
-
Discuss the updated Ontario guidelines for HPV testing and screening
-
Develop effective strategies to counsel patients on HPV prevention
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
vendredi express : 15 min top chrono !
Dépistage et Immunisation du VPH : Une stratégie complète pour les patients
Objectifs d'apprentissage
-
Reconnaître l’importance de la prévention du VPH
-
Discuter des lignes directrices mises à jour de l’Ontario en ce qui concerne les tests de dépistage du VPH
-
Développer des stratégies efficaces pour conseiller les patients à propos de la vaccination contre le VPH
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
Navigating the Diabetes Canada Guidelines: Practical Tips to provide quality diabetes care when time is limited
Learning Objectives
By the end of this On Demand webinar, health care providers will be able to effectively improve health outcomes in people living with diabetes by:
-
Recognizing metrics from sensor-based glucose technology to direct therapy modification.
-
Applying a step wise approach to diabetes care to simplify individualized treatment plans.
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
15 minute fridays
Skin POOP (Pain out of Proportion)
Learning Objectives
-
Recognize pain out of proportion as a Red Flag
-
Discuss the major skin pain out of proportion conditions
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
vendredi express : 15 min top chrono !
Douleurs disproportionnées de la peau
Objectifs d'apprentissage
-
Reconnaitre les douleurs disproportionnées de la peau comme un signal d’alert
-
Discuter des principales affections cutanées associées aux douleurs disproportionnées de la peau
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
15 minute fridays
Anaphylaxis 2025: Fast Action, Smarter Care
Learning Objectives
-
Recognize the clinical features of anaphylaxis and apply a definition to support timely diagnosis in primary care settings.
-
Demonstrate appropriate use of epinephrine, including dosing based on patient weight and indications for repeat administration.
-
Support patient education and decision-making by addressing common barriers to epinephrine use and promoting safe, informed self-management.
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
vendredi express : 15 min top chrono !
L'anaphylaxie 2025 : Action rapide, soins intelligents
Objectifs d'apprentissage
-
Reconnaître les symptômes cliniques de l’anaphylaxie et mettre en pratique une définition fondée sur des données probantes pour appuyer le diagnostic rapide dans un contexte de soins primaires.
-
Démontrer l’utilisation appropriée de l’épinéphrine, notamment la posologie en fonction du poids du patient et les indications associées à l’administration répétée
-
Contribuer à la sensibilisation des patients et à la prise de décisions en abordant les obstacles courants à l’utilisation de l’épinéphrine et en faisant la promotion d’une autoprise en charge sécuritaire et éclairée.
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
Navigating the Diabetes Canada Guidelines: Practical tips to provide quality diabetes care when time is limited
Empty space, drag to resize
Learning Objectives
By the end of this 45-minute webinar, health care providers will be able to effectively improve health outcomes in people living with diabetes by:
-
Recognizing metrics from sensor-based glucose technology to direct therapy modification.
-
Applying a step wise approach to diabetes care to simplify individualized treatment plans.
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
Études de cas: Le diabète de type 2 et la surveillance du glucose par capteur
Objectifs d'apprentissage
-
Reconnaître la valeur ajoutée de la surveillance du glucose par capteur, à l’aide des concepts du temps dans la plage cible et de la variabilité glycémique.
-
Illustrer les bienfaits cliniques de l’utilisation des nouvelles technologies dans la prise en charge d’un vaste éventail de personnes vivant avec le diabète de type 2.
-
Utiliser les valeurs obtenues par les profils glycémiques ambulatoires de patients pour optimiser la pharmacothérapie et le traitement global du diabète.
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
Learning Objectives | Kidney 2025 Conference
At the conclusion of this On Demand program, attendees will be able to:
-
Communicate atypical cues for diagnosing and safe selection of pharmacotherapies for CKD
-
List the immunization principles for CKD
-
Describe the pathophysiology of and discuss the emerging therapies targeting inflammation in kidney disease
-
Differentiate between the therapeutic strategies for lipid disorders and obesity in kidney disease
-
Recall the kidney-heart interactions and discriminate between traditional and new cardiorenal treatment pillars
-
Summarize the remedies for renal angiomyolipomas and recommend when to refer
-
Recognize the signs of primary glomerular disease and offer management options
-
Identify and develop treatment approaches for nephrotoxicity
-
Explore responsible and effective implementation of AI to enhance kidney disease care across healthcare settings.
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
15 minute fridays
Addressing the Rise in HPV-related Head and Neck Cancers: The Importance of HPV Prevention in Males
Learning Objectives
-
Recognize the factors leading to the rising incidence of head and neck cancers in males
-
Develop communication strategies for effective HPV prevention discussions with males
-
Assess practical approaches to integrate HPV prevention into clinical practice
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
vendredi express : 15 min top chrono !
Freiner la hausse des cas de cancers de la tête et du cou associés au VPH : l’importance de la prévention du VPH chez les hommes
Objectifs d'apprentissage
-
Reconnaître les facteurs à l’origine de l’augmentation des cas de cancers de la tête et du cou chez les hommes
-
Élaborer des stratégies de communication pour avoir des discussions efficaces sur la prévention du VPH avec les hommes
-
Évaluer des approches concrètes pour intégrer la prévention VPH dans la pratique clinique
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
15 minute fridays
Perimenopause: From Symptoms to Solutions
Learning Objectives
-
Identify the signs and symptoms of perimenopause
-
Apply evidence-based treatment strategies to manage associated symptoms effectively
Empty space, drag to resize
Empty space, drag to resize
vendredi express : 15 min top chrono !
La périménopause : Comprendre les symptômes et les options de traitement
Objectifs d'apprentissage
-
Identifier les signes et les symptômes de la périménopause
-
Appliquer des stratégies de traitement fondées sur des données probantes pour gérer efficacement les symptômes associés
Empty space, drag to resize